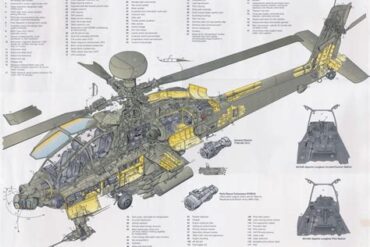
The Indian Air Force (IAF) plays a crucial role in national security, utilizing a range of aircraft to ensure operational readiness. Among these aircraft, helicopters serve various critical functions, including combat, reconnaissance, transport, and humanitarian assistance. This guide delves into the different types of helicopters operated by the IAF, their specifications, roles, and significance in modern warfare.
1. Evolution of Helicopter Operations in the IAF
The IAF has a rich history of helicopter operations, dating back to the late 1950s when it inducted its first helicopters. Initially, the IAF primarily utilized helicopters for transport and medical evacuation. However, over the decades, the role of helicopters has evolved significantly. Modern IAF helicopters are equipped with advanced technology, enhancing their operational capabilities in combat and other critical missions.
1.1 Early Years: Induction of the First Helicopters
The first helicopters introduced into the IAF were the Westland Wapiti and the Piaggio P.149D. These aircraft marked the beginning of rotary-wing operations in the IAF, primarily used for reconnaissance and logistical support.
1.2 Growth and Development
As conflicts and operational requirements evolved, the IAF expanded its helicopter fleet. The introduction of the HAL Cheetah and HAL Dhruv in the 1970s and 1980s marked a significant advancement in rotary-wing capabilities. These helicopters played vital roles in high-altitude operations, disaster relief, and troop transport.
2. Types of Helicopters in the IAF Fleet
The IAF operates a diverse range of helicopters, each tailored to specific operational requirements. These helicopters can be categorized into several key types:
2.1 Utility Helicopters
Utility helicopters are designed for versatile operations, including troop transport, cargo movement, and medical evacuation. The HAL Dhruv and Mil Mi-8 are prominent examples of utility helicopters in the IAF.
HAL Dhruv
The HAL Dhruv is an indigenously developed utility helicopter that boasts advanced avionics and systems. With a capacity to carry up to 16 passengers, it is ideal for various missions, including search and rescue, air ambulance, and VIP transport.
Mil Mi-8
The Mil Mi-8 is a medium twin-turbine helicopter widely used for transport operations. Its robust design and large cargo capacity make it an essential asset for the IAF in logistical support and troop movement.
2.2 Attack Helicopters
Attack helicopters are specially designed for engaging ground targets and supporting ground forces. The HAL Rudra and AH-64 Apache are the primary attack helicopters in the IAF inventory.
HAL Rudra
The HAL Rudra is a versatile attack helicopter equipped with state-of-the-art weapon systems. It features advanced avionics and multi-role capabilities, enabling it to perform anti-tank, air-to-air, and close air support missions.
AH-64 Apache
The AH-64 Apache is a combat-proven attack helicopter known for its agility and firepower. Equipped with precision weapons and advanced targeting systems, the Apache significantly enhances the IAF’s strike capabilities against enemy ground forces.
2.3 Reconnaissance and Surveillance Helicopters
These helicopters are crucial for gathering intelligence and conducting reconnaissance missions. The HAL Cheetah and Chetak are notable examples.
HAL Cheetah
The HAL Cheetah is known for its high-altitude performance, making it ideal for surveillance in mountainous regions. Its agility and capability to operate in challenging environments make it a valuable asset for reconnaissance missions.
Chetak Helicopter
The Chetak, derived from the Alouette III, is primarily used for surveillance and reconnaissance. It is equipped with modern navigation systems and is capable of performing long-range missions.
2.4 Transport Helicopters
Transport helicopters are vital for moving troops and equipment in various terrains. The Mil Mi-17 series is the backbone of the IAF’s transport capabilities.
Mil Mi-17
The Mil Mi-17 is a versatile helicopter used for tactical troop transport, medical evacuation, and logistical support. Its large cabin and robust design allow it to carry heavy loads in challenging environments.
3. Advanced Features of IAF Helicopters
The helicopters operated by the IAF are equipped with cutting-edge technology, enhancing their operational effectiveness. Key advanced features include:
3.1 Avionics and Navigation Systems
Modern IAF helicopters are equipped with advanced avionics systems that include digital cockpits, multi-functional displays, and GPS navigation. These systems improve situational awareness, ensuring pilots can operate effectively in diverse conditions.
3.2 Weapon Systems
IAF attack helicopters are armed with an array of advanced weaponry, including missiles, rockets, and cannons. The integration of precision-guided munitions enables helicopters to engage targets with high accuracy, minimizing collateral damage.
3.3 Communication Systems
Robust communication systems allow seamless coordination between helicopters and ground forces. Advanced communication links facilitate real-time information sharing, improving mission success rates.
4. Operational Roles of Helicopters in the IAF
Helicopters play multifaceted roles in the IAF, contributing significantly to various operational missions:
4.1 Combat Operations
In combat scenarios, helicopters provide essential support to ground forces. Attack helicopters engage enemy positions, while utility helicopters facilitate troop movement and logistical support.
4.2 Search and Rescue Missions
Helicopters are crucial for conducting search and rescue operations, particularly in disaster-affected areas or remote regions. Their agility and ability to land in confined spaces make them ideal for rescuing individuals in distress.
4.3 Humanitarian Assistance
During natural disasters, helicopters are deployed for humanitarian assistance missions. They transport relief supplies, conduct aerial surveys, and provide medical evacuations, showcasing their versatility beyond military operations.
5. Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their significant contributions, the IAF faces challenges in helicopter operations. These include:
5.1 Maintenance and Upgrades
The maintenance of an extensive helicopter fleet poses logistical challenges. Upgrading older helicopters to meet modern standards is essential for maintaining operational readiness.
5.2 Technological Advancements
The rapid evolution of technology necessitates continuous updates to avionics and weapon systems. The IAF must invest in research and development to keep pace with global advancements.
5.3 Strategic Partnerships
Collaborating with international defense manufacturers can enhance the capabilities of IAF helicopters. Strategic partnerships allow access to advanced technology and expertise, ensuring that the IAF remains at the forefront of helicopter operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, helicopters are an indispensable component of the Indian Air Force, playing vital roles in combat, reconnaissance, and humanitarian missions. As the IAF continues to modernize its helicopter fleet, the emphasis on advanced technology and strategic partnerships will be crucial for maintaining operational effectiveness. The future of helicopter operations in the IAF looks promising, ensuring that these flying machines remain a formidable asset in the defense of the nation.