Military helicopters are an indispensable component of modern warfare, combining speed, agility, and versatility to meet the complex demands of military operations. This guide aims to provide an extensive overview of military helicopters, covering their types, functionalities, advancements in technology, and their roles in various military scenarios.
1. Understanding Military Helicopters
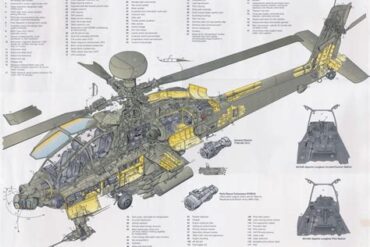
Military helicopters are rotary-wing aircraft specifically designed for military purposes. They are utilized for a myriad of functions including transport, reconnaissance, search and rescue, and combat. These aircraft are characterized by their ability to hover, take off, and land vertically, making them suitable for operations in confined spaces where traditional fixed-wing aircraft would struggle.
1.1 Key Components of Military Helicopters
Military helicopters consist of several critical components that enhance their performance:
-
Rotors: The primary lift-generating component. Helicopters typically have one main rotor and may also have a tail rotor or multiple rotors.
-
Fuselage: The body of the helicopter, which houses the cockpit, crew, and cargo.
-
Landing Gear: Designed for stability during landings and takeoffs. Military helicopters often have retractable gear for better aerodynamics.
-
Avionics: Advanced electronic systems that provide navigation, communication, and targeting capabilities. Modern avionics systems improve situational awareness and operational efficiency.
2. Types of Military Helicopters
Military helicopters can be categorized into several types based on their roles and capabilities. Understanding these types is essential for grasping their unique contributions to military operations.
2.1 Attack Helicopters
Attack helicopters are heavily armed and designed primarily for engaging ground targets. They feature advanced targeting systems and can carry a variety of weaponry, including missiles and machine guns. Notable examples include the AH-64 Apache and the Mil Mi-24. These helicopters are often used in close air support, tank hunting, and anti-insurgency operations.
2.2 Transport Helicopters
Transport helicopters are designed to transport troops, equipment, and supplies. They can carry large payloads and are essential for logistical support during military operations. The CH-47 Chinook and UH-60 Black Hawk are prime examples. Their versatility allows for rapid troop deployment and extraction in diverse environments.
2.3 Utility Helicopters
Utility helicopters serve multiple roles, including reconnaissance, medical evacuation (MEDEVAC), and support for other aircraft. The Bell UH-1 Iroquois, known as the “Huey,” is one of the most iconic utility helicopters, having been extensively used during the Vietnam War.
2.4 Reconnaissance Helicopters
Reconnaissance helicopters are equipped with advanced sensors and cameras to gather intelligence on enemy positions and movements. They play a crucial role in surveillance missions, providing real-time data to ground troops and command centers. The OH-58 Kiowa is a notable reconnaissance helicopter that has been employed in various combat scenarios.
3. The Role of Military Helicopters in Combat Operations
Military helicopters play a vital role in combat operations by enhancing the effectiveness of ground forces and providing air support in dynamic battlefields. Their agility and speed allow them to respond quickly to changing combat conditions.
3.1 Close Air Support (CAS)
In CAS missions, attack helicopters provide direct support to ground troops engaged in combat. They are capable of delivering precision strikes against enemy forces while minimizing collateral damage. The ability to hover and maneuver in tight spaces allows these helicopters to engage targets that may be difficult for fixed-wing aircraft to reach.
3.2 Combat Search and Rescue (CSAR)
Military helicopters are often employed in CSAR missions to locate and recover downed pilots or stranded soldiers in hostile territory. Equipped with medical facilities and defensive armaments, they can extract personnel while providing cover against enemy fire. The HH-60 Pave Hawk is a prime example of a helicopter designed specifically for CSAR operations.
3.3 Troop Insertion and Extraction
Transport helicopters are essential for inserting and extracting troops in combat zones. They can land in confined spaces, allowing special forces to be deployed quickly and effectively. This capability is particularly valuable in urban warfare, where traditional ground vehicles may be hindered.
4. Technological Advancements in Military Helicopters
The evolution of military helicopters has been significantly influenced by technological advancements. These innovations enhance their operational capabilities, survivability, and effectiveness in combat situations.
4.1 Advanced Avionics and Navigation Systems
Modern military helicopters are equipped with state-of-the-art avionics systems that improve navigation and targeting. Global Positioning System (GPS) technology enables precise positioning, while advanced radar and sensor systems provide enhanced situational awareness. These features are critical for conducting operations in low-visibility conditions or hostile environments.
4.2 Stealth Technology
The integration of stealth technology in military helicopters helps reduce their radar signature, making them harder to detect. This is particularly important for helicopters conducting reconnaissance or strike missions deep behind enemy lines. The Sikorsky RAH-66 Comanche was designed with stealth features, showcasing the trend towards low-observable aircraft.
4.3 Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
While not traditional helicopters, UAVs are increasingly being utilized in military operations, providing reconnaissance and surveillance capabilities without putting pilots at risk. Some military helicopters are now designed to operate in conjunction with UAVs, enhancing the overall effectiveness of aerial operations.
5. Military Helicopter Training and Operations
The effective use of military helicopters hinges on rigorous training and operational procedures. Pilots and crew undergo extensive training programs to ensure they can operate these complex machines safely and effectively in combat situations.
5.1 Pilot Training
Pilot training for military helicopters is comprehensive, encompassing various flight maneuvers, navigation techniques, and emergency procedures. Training programs often include simulator exercises to prepare pilots for real-world scenarios, including night operations and adverse weather conditions.
5.2 Maintenance and Support
Maintaining military helicopters requires a skilled workforce and robust logistical support. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the reliability and safety of these aircraft. Military forces invest in specialized training for maintenance personnel to handle the unique systems found in modern helicopters.
6. Challenges Faced by Military Helicopters
Despite their many advantages, military helicopters face several challenges that can impact their effectiveness in combat operations.
6.1 Vulnerability to Enemy Fire
Helicopters are vulnerable to small arms fire and anti-aircraft weapons. Their low altitude and slow speed compared to fixed-wing aircraft can make them susceptible to enemy fire during combat operations. As a result, modern helicopters are equipped with defensive systems to counteract these threats.
6.2 Operational Limitations
Environmental factors such as weather and terrain can significantly impact helicopter operations. High-altitude environments or adverse weather conditions can limit their effectiveness and operational range. Pilots must be trained to navigate these challenges effectively to ensure mission success.
7. Future Trends in Military Helicopters
As military needs evolve, so too do the designs and capabilities of helicopters. The future of military helicopters is likely to be shaped by several key trends.
7.1 Increased Automation
The integration of automation and artificial intelligence into military helicopters is expected to enhance operational efficiency. Automated flight systems can reduce pilot workload, allowing for more complex missions to be executed with fewer crew members.
7.2 Hybrid Propulsion Systems
Hybrid propulsion systems, which combine traditional engines with electric motors, are gaining attention as a means to improve fuel efficiency and reduce operational costs. These systems could enable longer flight times and greater operational flexibility.
7.3 Enhanced Armament Systems
Future military helicopters are likely to be equipped with more advanced weaponry, including precision-guided munitions and directed energy weapons. These enhancements will increase their combat effectiveness while minimizing collateral damage.
Conclusion
Military helicopters remain a cornerstone of modern military operations, providing critical capabilities that enhance the effectiveness of armed forces. As technology continues to advance, these aircraft will undoubtedly evolve, adapting to meet the challenges of future warfare. Understanding the various types, roles, and technological advancements of military helicopters is essential for comprehending their significance in contemporary combat scenarios.