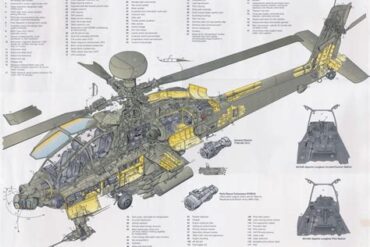
Utility helicopters, often referred to as multipurpose helicopters, are versatile aircraft that serve a broad range of functions, from military operations to civilian tasks. These helicopters are designed to transport personnel, equipment, and supplies, perform medical evacuations, and conduct search and rescue missions, among other duties. Their adaptability, combined with advanced technology, makes them indispensable assets in both peacetime and combat scenarios.
Utility helicopters have evolved significantly since their inception. Initially developed during World War II, these aircraft have undergone continuous improvements to enhance their performance, survivability, and mission capabilities. Today, they play a crucial role in modern military operations and civilian applications, providing vital support in various situations.
Key Features of Utility Helicopters
Versatility and Multi-role Capabilities
One of the defining characteristics of utility helicopters is their versatility. These aircraft are designed to perform multiple roles, which makes them highly valuable in diverse operational environments. Whether it’s transporting troops to a remote location, delivering humanitarian aid, or conducting reconnaissance missions, utility helicopters can adapt to a wide range of tasks.
Utility helicopters are equipped with modular systems that allow for quick configuration changes. For instance, a helicopter configured for troop transport can be rapidly reconfigured for medical evacuation (MEDEVAC) by installing stretcher kits and medical equipment. This flexibility is crucial in dynamic environments where mission requirements can change rapidly.
Advanced Avionics and Navigation Systems
Modern utility helicopters are equipped with state-of-the-art avionics and navigation systems that enhance their operational capabilities. These systems include advanced flight control systems, GPS navigation, terrain-following radar, and night vision capabilities. These features enable utility helicopters to operate in challenging conditions, such as adverse weather and low-visibility environments.
The integration of digital cockpit displays and automated flight management systems also improves situational awareness for pilots, allowing them to focus on mission objectives while reducing workload. Additionally, some utility helicopters are equipped with autopilot systems that can assist in complex flight maneuvers, further enhancing safety and efficiency.
Load Capacity and Range
Utility helicopters are designed to carry significant payloads over extended distances. The load capacity of these aircraft varies depending on the model, with some capable of transporting up to 20 passengers or several tons of cargo. This makes them ideal for missions that require the movement of large numbers of personnel or heavy equipment.
In terms of range, utility helicopters are engineered to cover considerable distances without the need for refueling. Some models are equipped with external fuel tanks that can extend their operational range, enabling them to reach remote or inaccessible areas. This capability is particularly valuable in search and rescue missions or during natural disasters when access to fuel may be limited.
Applications of Utility Helicopters
Military Operations
Utility helicopters play a critical role in military operations, providing essential support across various mission types. They are commonly used for troop transport, logistical support, medical evacuation, and reconnaissance. In combat situations, utility helicopters can be armed with weapons systems, such as machine guns and rocket pods, to provide close air support to ground forces.
The ability to operate in diverse environments, from deserts to mountainous terrain, makes utility helicopters invaluable in modern warfare. They are often deployed in joint operations with other aircraft, such as attack helicopters and fixed-wing planes, to achieve mission objectives. Additionally, utility helicopters are used for special operations missions, where their speed, agility, and stealth capabilities are crucial for success.
Search and Rescue (SAR)
Utility helicopters are indispensable in search and rescue (SAR) operations, where they provide rapid response and access to remote or difficult-to-reach areas. These helicopters are equipped with specialized equipment, such as hoists, winches, and thermal imaging cameras, to locate and extract individuals in distress.
SAR operations often require utility helicopters to operate in challenging conditions, such as mountainous terrain, dense forests, or over open water. The combination of advanced avionics, powerful engines, and durable airframes allows these helicopters to perform under demanding circumstances, saving lives in the process.
Medical Evacuation (MEDEVAC)
Medical evacuation is another critical application of utility helicopters. In emergency situations, these helicopters can rapidly transport injured or critically ill patients to medical facilities, often making the difference between life and death. MEDEVAC helicopters are typically equipped with medical equipment, such as ventilators, defibrillators, and intravenous infusion systems, to provide in-flight care.
The ability to land in confined spaces, such as urban areas or disaster zones, makes utility helicopters ideal for MEDEVAC missions. Additionally, their speed and range allow them to cover large distances quickly, ensuring that patients receive timely medical attention.
Humanitarian Aid and Disaster Relief
Utility helicopters are frequently deployed in humanitarian aid and disaster relief efforts, where they deliver essential supplies, such as food, water, and medical supplies, to affected areas. In the aftermath of natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, or hurricanes, these helicopters can access regions that are cut off from traditional transportation networks.
In addition to delivering supplies, utility helicopters can also be used to evacuate individuals from disaster zones, transport emergency response teams, and conduct aerial surveys to assess damage. Their versatility and adaptability make them vital assets in humanitarian missions, helping to alleviate suffering and support recovery efforts.
Civilian and Commercial Applications
Beyond military and humanitarian uses, utility helicopters also have a wide range of civilian and commercial applications. They are used in industries such as construction, oil and gas, forestry, and law enforcement. For example, utility helicopters can be used to transport workers to offshore oil rigs, conduct aerial inspections of power lines, or support firefighting efforts by delivering water and fire retardants.
In law enforcement, utility helicopters are used for aerial surveillance, traffic monitoring, and pursuit operations. Their ability to cover large areas quickly and provide real-time information to ground units makes them invaluable tools for maintaining public safety and security.
Top Utility Helicopter Models
Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk
The Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk is one of the most well-known utility helicopters in the world. Developed for the United States Army, the Black Hawk has been in service since the late 1970s and has proven its effectiveness in a wide range of missions. It is capable of carrying 11 troops with equipment or up to 9,000 pounds of cargo. The Black Hawk is also equipped with advanced avionics, night vision systems, and self-defense measures, making it a formidable asset in both combat and non-combat scenarios.
Bell UH-1 Iroquois (Huey)
The Bell UH-1 Iroquois, commonly known as the Huey, is a legendary utility helicopter that played a pivotal role during the Vietnam War. The Huey was the first turbine-powered helicopter to enter production for the U.S. military, and its versatility made it the backbone of many operations. The UH-1 can be used for troop transport, medical evacuation, and cargo delivery. Although it has been largely replaced by more modern helicopters, the Huey remains in service in several countries and continues to be a symbol of rotary-wing aviation.
Eurocopter EC725 Caracal
The Eurocopter EC725 Caracal, also known as the H225M, is a long-range tactical transport helicopter developed by Airbus Helicopters. The Caracal is designed for combat search and rescue, medical evacuation, and troop transport missions. It is capable of carrying up to 29 troops or 12 stretchers, and it has a maximum takeoff weight of 24,250 pounds. The EC725 is equipped with advanced avionics, including a glass cockpit and automated flight control systems, making it a highly capable and reliable utility helicopter.
AgustaWestland AW101
The AgustaWestland AW101, also known as the Merlin, is a medium-lift utility helicopter that has been widely adopted by military forces around the world. The AW101 is capable of performing a wide range of missions, including troop transport, search and rescue, and anti-submarine warfare. It can carry up to 30 troops or 12 stretchers, and it is equipped with advanced sensors, avionics, and defensive systems. The AW101’s three-engine configuration provides excellent power and redundancy, allowing it to operate in challenging environments.
Mil Mi-8/17
The Mil Mi-8, and its modernized variant, the Mi-17, is a Soviet-designed medium twin-turbine helicopter that has been in service since the 1960s. The Mi-8/17 series is one of the most widely produced helicopters in the world, with over 17,000 units built. It is used by both military and civilian operators in more than 50 countries. The Mi-8/17 is known for its ruggedness, reliability, and ability to operate in extreme conditions, making it a popular choice for missions ranging from troop transport to disaster relief.
Conclusion
Utility helicopters are indispensable assets that provide critical support in a wide range of missions, from military operations to civilian applications. Their versatility, advanced technology, and ability to operate in diverse environments make them essential tools for modern aviation. As technology continues to evolve, utility helicopters will remain at the forefront of rotary-wing aviation, adapting to meet the challenges of the future.